Topic outline
-
-
-
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
A semipermeable membrane is a thin membrane that will pass certain small molecules, but not others.
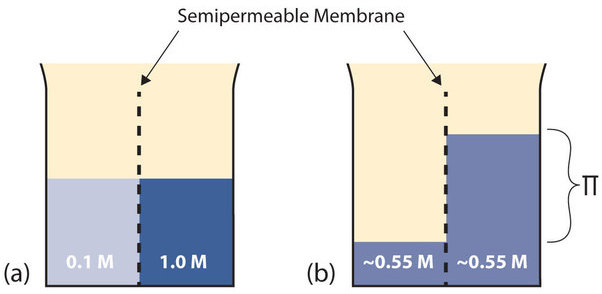
Figure 1: (a) Two solutions of differing concentrations are placed on either side of a semipermeable membrane. (b) When osmosis occurs, solvent molecules selectively pass through the membrane from the dilute solution to the concentrated solution, diluting it until the two concentrations are the same.
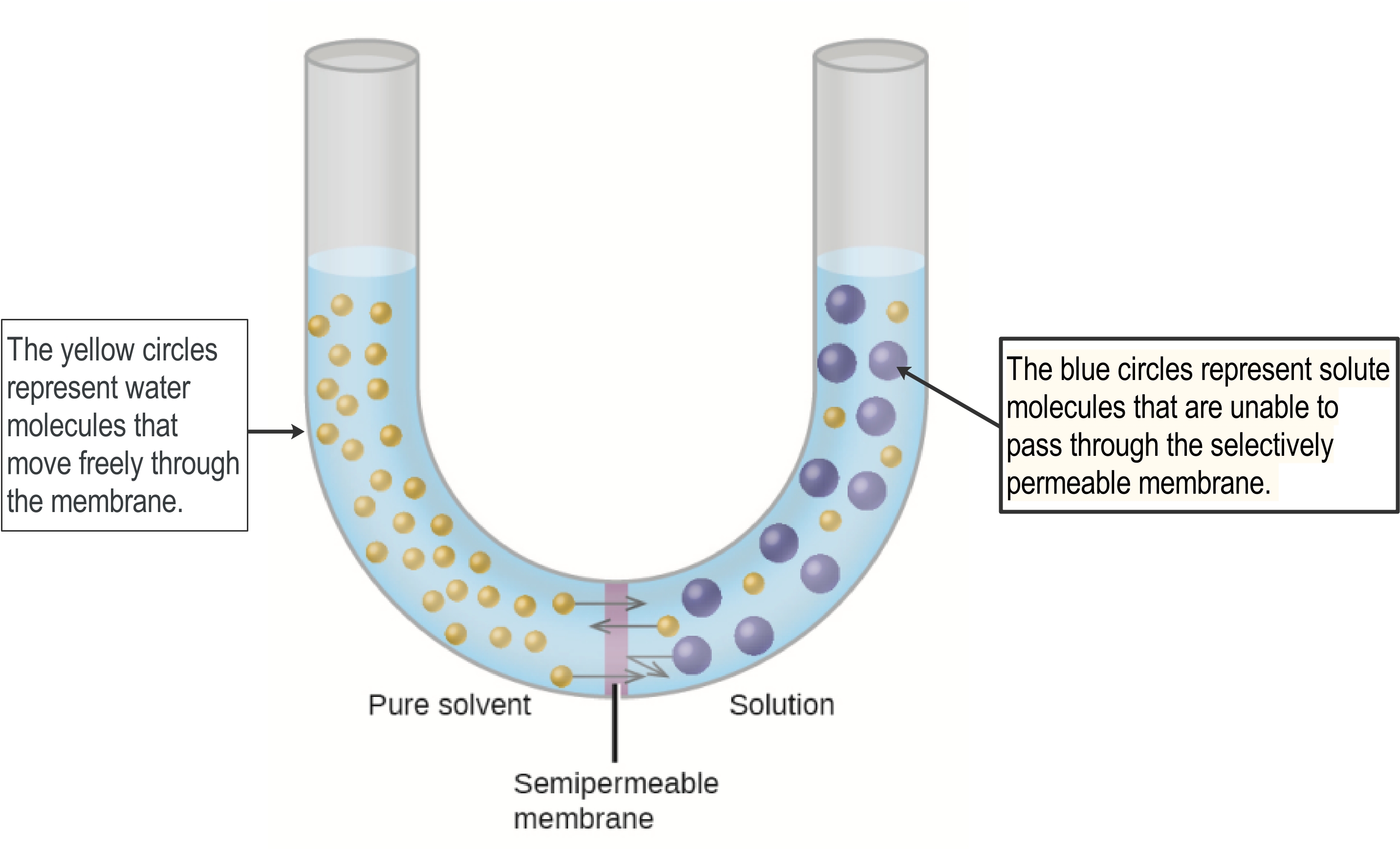
Figure 2: There is movement of water molecules through the membrane, but the blue molecules cannot get through the membrane so do not move.
Activity 1
Click on the link below:
Watch the water molecules move in this osmosis simulation. This simulation shows why there is a net flow of water through a semi-permeable membrane from the side with a low solute concentration to the side with a high solute concentration.
Eventually, the concentration either side of the membrane will be the same. At this point, there will be equal movement of water molecules in both directions. The solution is said to be in equilibrium – there is therefore no net movement in one direction.
Osmosis in cells
The results of osmosis are different in plant and animal cells.
Plant cells
Plant cells have a strong cellulose cell wall on the outside of the cell membrane. This supports the cell and stops it bursting when it gains water by osmosis.
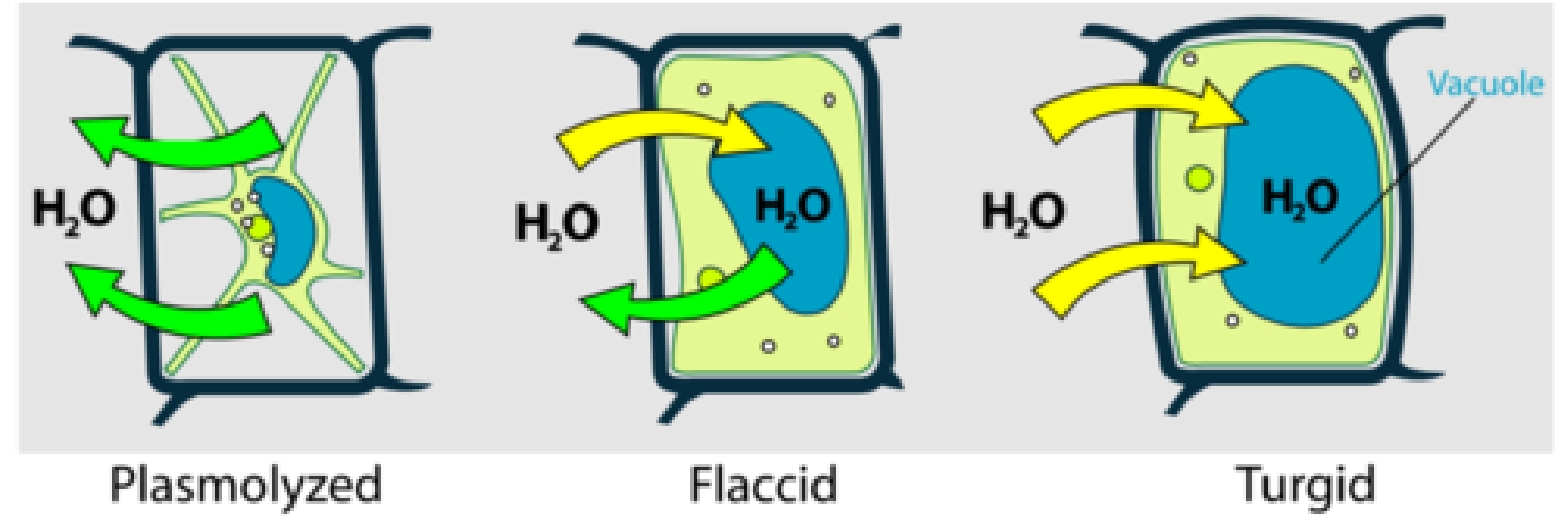
Water enters the cell by osmosis. The cytoplasm pushes against the cell wall and the cell becomes turgid. Turgid plant cells play an important part in supporting the plant.
Water leaves the cell by osmosis. The cytoplasm shrinks and pulls away from the cell wall. This process is called plasmolysis. The cell becomes flaccid and the plant wilts.
Animal cells
Animal cells do not have a cell wall. They change size and shape when put into solutions that are at a different concentration to the cell contents. For example, red blood cells:
- gain water, swell and burst in a more dilute solution
- lose water and shrink in a more concentrated solution (they become wrinkled)
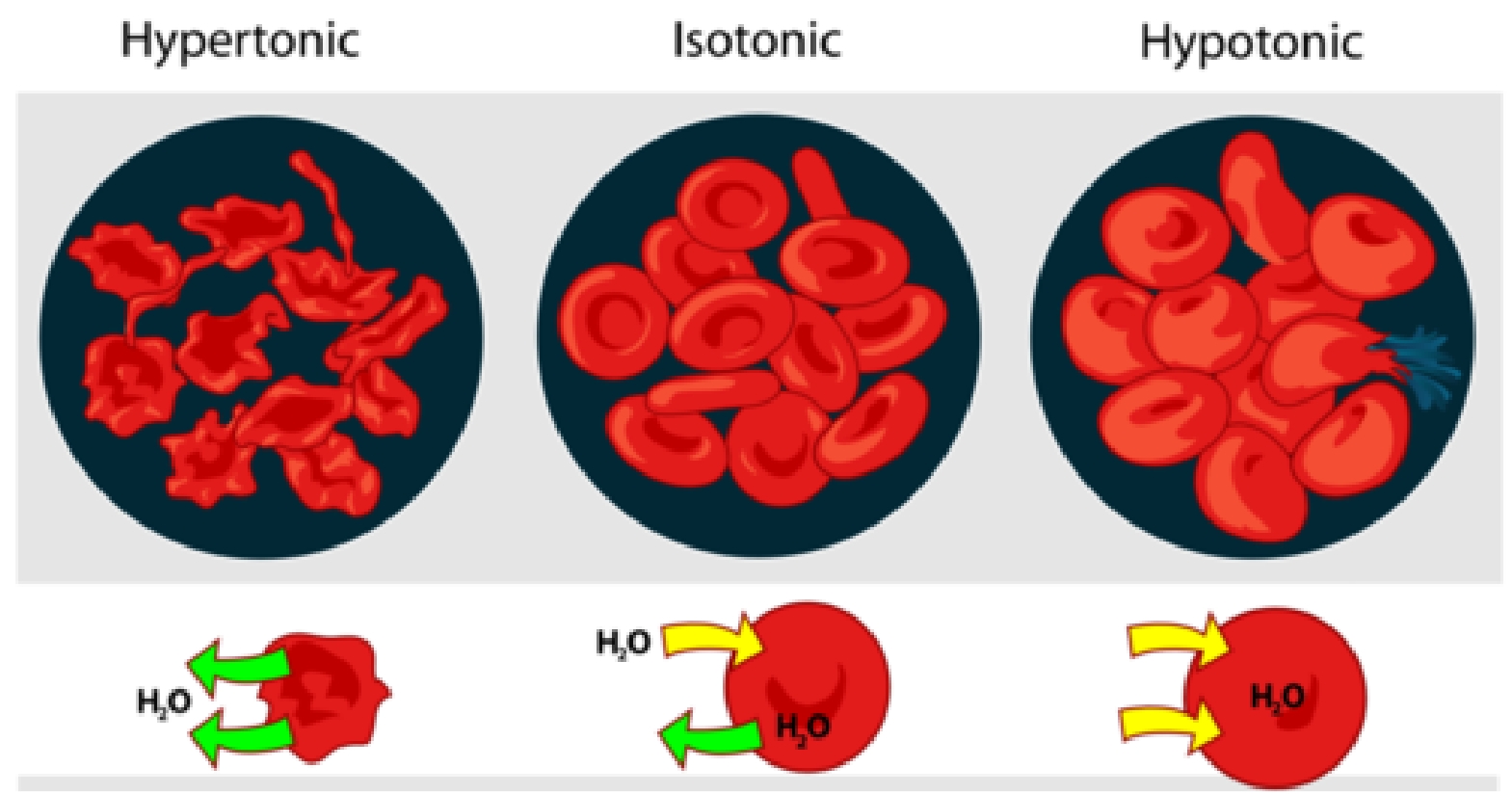
These things do not happen inside the body. Osmoregulation involving the kidneys ensures that the concentration of the blood stays about the same as the concentration of the cell contents.
-